Passive houses are revolutionizing the way we think about energy efficiency in home building. These super-insulated, airtight structures drastically reduce energy consumption, offering a sustainable alternative for the future.
Here are ten reasons why passive houses are leading the charge in eco-friendly living.
Passive houses use around 90% less energy than traditional homes. By focusing on minimizing energy usage rather than just producing green energy, passive houses achieve remarkable efficiency. This is accomplished through high-performance insulation, airtight construction, and strategic design.

Standard windows account for 25% to 30% of residential energy loss. Passive houses use triple-pane, high-performance windows that are strategically oriented to maximize natural light and warmth while minimizing heat loss.
- Region Specific: In colder climates, these windows keep the heat in; in warmer climates, they prevent excess heat from entering.
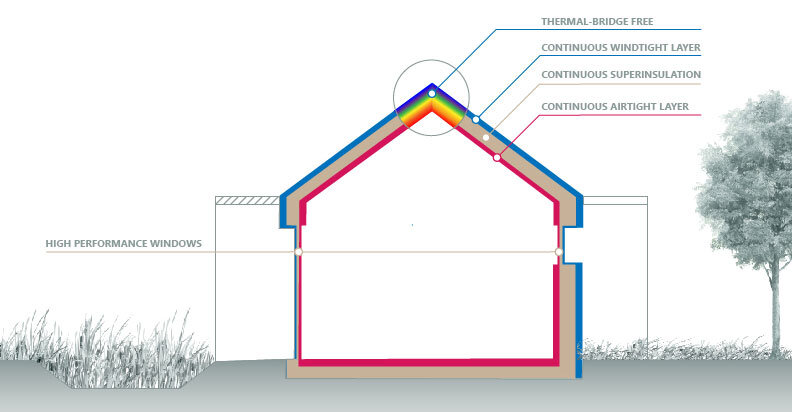
An airtight building envelope prevents air leakage, maintaining a stable indoor temperature. This reduces the need for heating and cooling, significantly cutting down energy use.
Passive houses are built with thick, climate-appropriate insulation. This can include walls, roofs, and even floors made from insulating materials, ensuring minimal heat transfer.
For this to work properly, it must be done based on the specific region. In warmer climates, additional shading and appropriate window selections are used to combat heat gain.
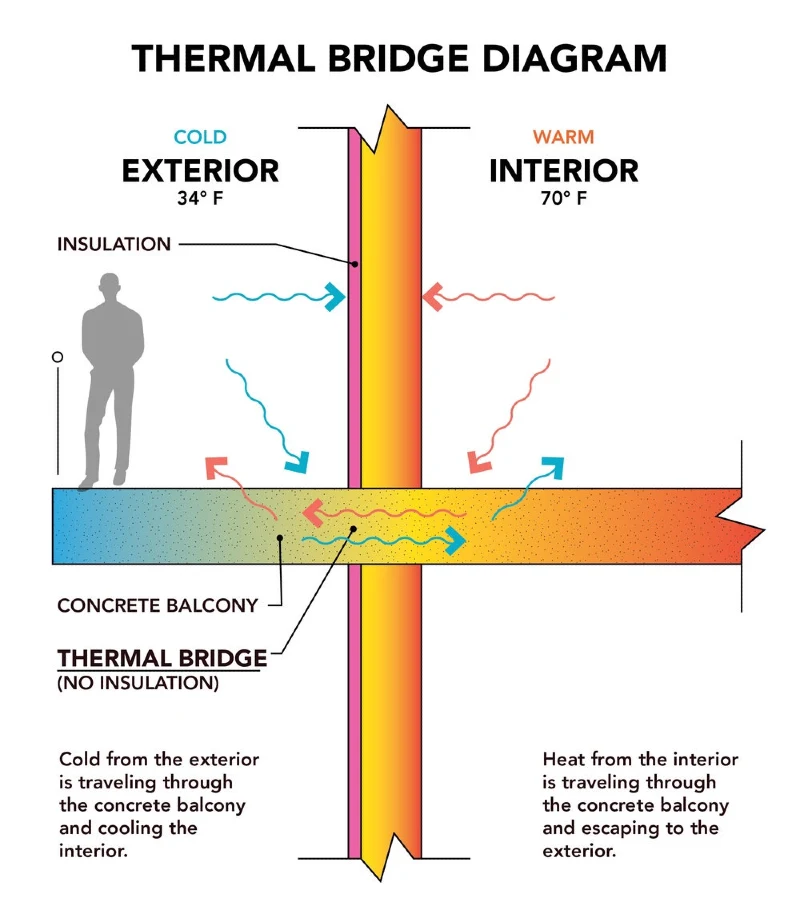
Thermal bridges are weak points in the insulation where heat can escape. Basically, these are spots where heat flows through the insulation, causing energy loss and reducing thermal efficiency. It typically occurs at junctions between walls, floors, and roofs, or around windows and doors.
Passive houses eliminate these weak points through continuous layers of insulation, keeping the building’s thermal integrity intact.
- Continuous Insulation: The insulation must cover the entire building envelope without gaps or interruptions.
- Thermal Breaks: All materials used must have low thermal conductivity to separate components that would otherwise conduct heat.
- High-Performance Windows and Doors: All windows and doors must have good insulation properties and proper sealing.
- Attention to Details: Junctions and connections must be designed and constructed to prevent heat leaks.
- Air Tightness: The building must be airtight to prevent heat loss through drafts.
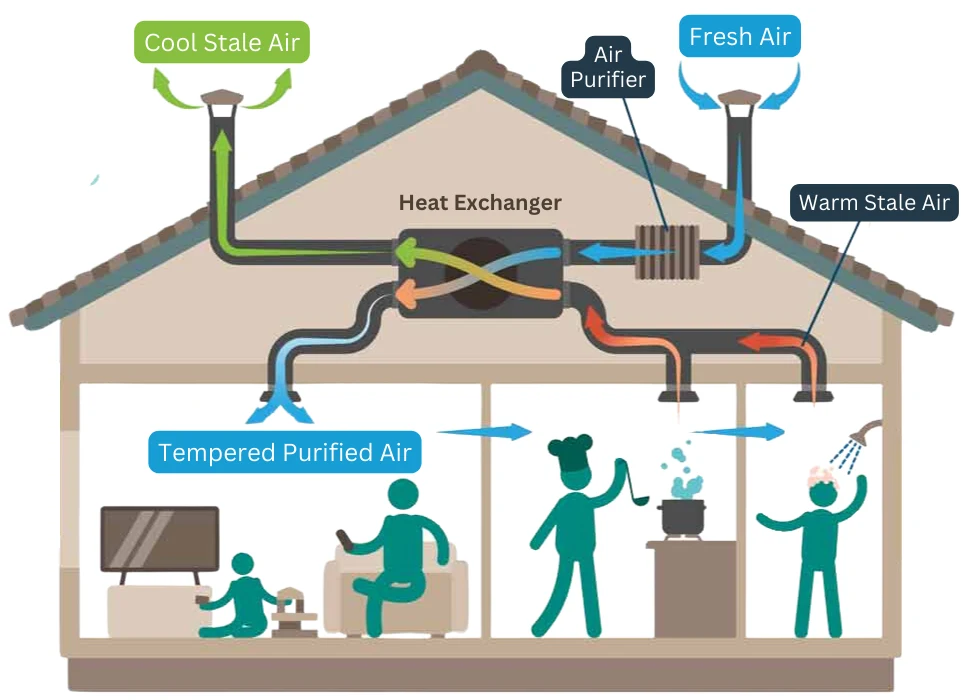
The airtight construction and continuous ventilation of passive houses result in superior indoor air quality. This reduces allergens and pollutants, creating a healthier living space.
Passive houses use heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems to maintain indoor air quality. These systems bring in fresh air while retaining the heat from outgoing air, ensuring efficient air circulation without energy loss. Beyond the sustainability angle, there’s also improved air quality and significant noise reduction inside the home.
While often associated with cold climates, passive houses offer benefits in all regions. Warm climates use different strategies, such as reflective materials and advanced shading, to achieve the same level of energy efficiency.
- Example: Passive houses in warmer climates use lighter colors and materials that reflect rather than absorb heat.
Although the initial investment in a passive house can be higher, the significant savings on energy bills make them cost-effective over time. Incentives like those from the Inflation Reduction Act can help offset initial costs substantially.
Passive houses are no longer limited to single-family homes. They are now being used for multifamily projects, dorms, and even skyscrapers. This expansion demonstrates the versatility and growing acceptance of passive house principles.

Conclusion
Passive houses represent the pinnacle of energy-efficient home building. By drastically reducing energy consumption, providing healthier living environments, and offering universal benefits, they’re paving the way for a more sustainable future. As technology and awareness continue to grow, passive houses are set to become a key player in combating climate change and promoting eco-friendly living.