The Rise and Fall of Enviva
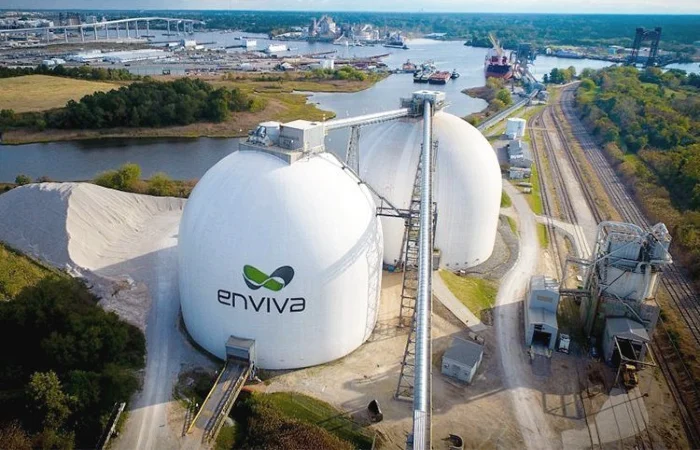
Enviva, once a titan in the biomass energy industry and the world’s largest producer of wood pellets, now teeters on the brink of collapse. Founded in 2004, this powerhouse harvested forests across the U.S. Southeast, fueling power plants in the EU, U.K., Japan, and South Korea. However, a series of catastrophic losses in the third quarter have seen Enviva’s stock plummet, its CEO replaced, and its very survival questioned.
Enviva’s story is a stark reminder of the volatile nature of the renewable energy market and the intricate balance between environmental sustainability and economic viability. This article delves into the rise and fall of Enviva, exploring the complexities and controversies that have led to its current predicament.
Biomass Energy Explained
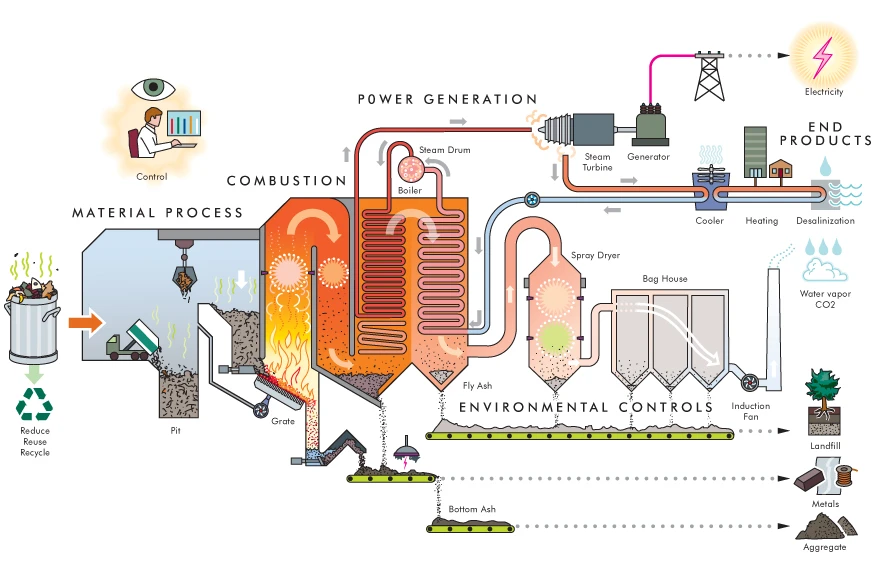
Biomass energy is a form of renewable energy derived from organic materials, such as wood, agricultural crops, and waste. These organic materials are referred to as biomass. The process of generating energy from biomass can be achieved through various methods, the most common being combustion.
In combustion, biomass is burned to produce heat. This heat is then used to boil water, creating steam that drives turbines, much like in a traditional power plant. The movement of the turbines generates electricity. Another method is gasification, where biomass is converted into a gas, which can then be burned to produce electricity or heat.
Biomass is considered renewable because the organic materials used can be replenished relatively quickly. For example, trees can be replanted and agricultural crops regrown each season. Additionally, biomass energy is often touted as carbon-neutral. This is based on the idea that the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the plants during their growth. However, this balance can be affected by the specific sources of biomass and the methods of harvesting and processing it.
Enviva’s Core Business Model and Operational Challenges
Enviva’s business model hinged on being a major player in the biomass energy sector, primarily through the production of wood pellets. These pellets, made from compressed organic matter or biomass, were marketed as a sustainable alternative to coal for electricity generation. Enviva’s target markets were primarily in Europe and Asia, where countries were transitioning away from fossil fuels to meet climate goals.

Operational Hurdles and Cost Challenges
Despite its initial success, Enviva faced significant operational challenges that contributed to its current struggles. One of the primary issues was the escalating cost of wood procurement. As demand for wood pellets increased, so did the competition for wood, driving up prices and squeezing Enviva’s profit margins.
Manufacturing complexities also played a role. The process of producing wood pellets is resource-intensive, involving cutting, drying, and compressing wood. These steps require significant energy inputs and efficient logistics, both of which became increasingly challenging and costly for Enviva.
Environmental Concerns and Regulatory Hurdles
Enviva’s operations also faced scrutiny from environmentalists and regulators. The company’s practices of sourcing wood from forests raised concerns about deforestation and its impact on biodiversity. Regulatory changes and increased environmental oversight in key markets added to the operational hurdles, further complicating Enviva’s business model.
The Controversy Surrounding Enviva's Green Claims
Whistleblower Revelations: A Crack in the Facade
Enviva’s environmental claims, central to its brand identity, faced a significant blow when a whistleblower came forward with revelations (and what appears to be concrete evidence) about its practices. Contrary to the company’s assertions of using only waste wood, the whistleblower alleged that Enviva was actually using whole trees for pellet production, driven to do so to meet the company’s own demand.
If true, this would contradict the company’s sustainability narrative and raise serious environmental concerns.

The Environmental Debate: Waste Wood vs. Whole Trees
The use of waste wood — such as sawdust and scraps from timber operations — is considered more environmentally sustainable, as it utilizes materials that would otherwise be discarded. However, the harvesting of whole trees for biomass energy is far more contentious. It leads to deforestation and habitat loss, and it negates the carbon-neutral advantage often claimed by biomass proponents. Whole tree harvesting also disrupts the carbon sequestration process, as mature trees are known to absorb significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.

Economic and Ecological Implications
The economic implications of Enviva’s practices are equally significant. The use of whole trees could potentially increase operational costs and impact profitability. Moreover, if Enviva’s sustainability claims are undermined, it could lead to a loss of consumer confidence and market share, particularly in environmentally conscious markets.
From an ecological perspective, the harvesting of whole trees raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of forests and the broader environmental impact. This controversy spotlights the delicate balance between renewable energy production and ecological preservation, challenging the very definition of what constitutes ‘sustainable’ biomass energy.
The Global Impact of Enviva's Downfall
Disruptions in the Biomass Energy Market
Enviva’s precarious position has far-reaching implications for the global biomass energy market. As the world’s largest wood pellet producer, its potential collapse will create a significant supply gap. This gap would particularly affect European and Asian countries that have come to rely on biomass as a key component of their renewable energy strategies.
The EU, for instance, has been a significant market for Enviva’s wood pellets, using them to meet renewable energy targets. A disruption in supply from Enviva could force these countries to reassess their energy portfolios, potentially leading to a temporary increase in fossil fuel use or a shift to other renewable sources.
Impact on Climate Change Goals
The situation with Enviva also poses challenges to climate change goals. Biomass energy, often touted as carbon-neutral, plays a critical role in the energy transition plans of many countries. The sudden unavailability of a major biomass source could lead to setbacks in achieving emission reduction targets, highlighting the need for diversified and resilient renewable energy strategies.
Economic Ripple Effects
Enviva’s struggles also have economic implications, both locally and internationally. In the U.S. Southeast, where Enviva sources much of its wood, there could be economic impacts on forestry and related industries. Internationally, countries heavily invested in biomass energy may face increased costs and logistical challenges in securing alternative renewable energy sources.
The Search for Alternatives
The potential collapse of Enviva underscores the importance of a diverse renewable energy portfolio. It highlights the need for investments in other renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower. This situation also serves as a call for innovation in the biomass sector, perhaps shifting focus to more sustainable practices and sources.
Financial Turmoil and Management Changes at Enviva
Enviva’s Financial Struggles
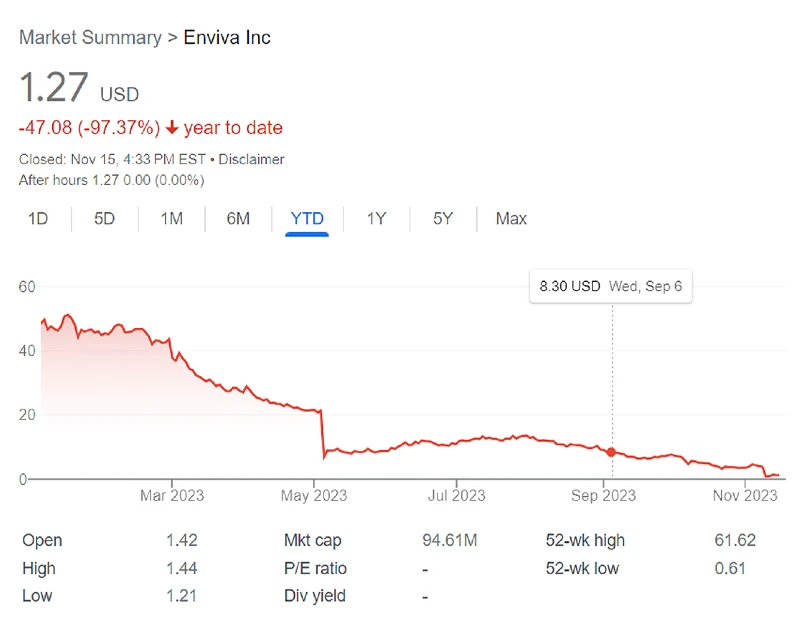
Enviva’s journey from a biomass behemoth to a company grappling with survival has been marked by severe financial challenges. The company faced a substantial downturn, with its stock prices plummeting and investors growing increasingly wary. This financial turmoil was primarily driven by escalating operational costs, market volatility, and the controversies surrounding its sustainability practices.
Management Shake-Up
In response to these challenges, Enviva underwent significant changes in its management structure. The most notable was the replacement of its CEO, signaling a strategic shift in an attempt to stabilize the company. This change at the top was part of a broader restructuring effort aimed at addressing the operational and financial issues plaguing Enviva.
Attempts to Steer the Company Back on Track
The new management embarked on a series of initiatives to salvage the company. These included efforts to streamline operations, reduce costs, and potentially diversify the business model. Part of this strategy involved exploring new markets and partnerships, as well as investing in more efficient and sustainable production technologies.
Impact on Employees and Stakeholders
The financial and managerial upheavals at Enviva had a profound impact on its employees and stakeholders. For employees, the uncertainty surrounding the company’s future created a tense working environment. Stakeholders, including suppliers and clients, were forced to reconsider their relationships and dependencies on Enviva, with some seeking alternative partners.
Environmental Advocacy and Opposition to Biomass Energy
Rising Voices Against Biomass
The controversies surrounding Enviva have amplified the voices of environmental groups and forest advocates who oppose large-scale biomass energy production. These groups argue that the environmental costs of biomass, especially practices like whole-tree harvesting, outweigh the purported benefits. They contend that such practices lead to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and increased carbon emissions — the very issues renewable energy seeks to mitigate.

Environmental Groups’ Critique
Environmental organizations have been vocal in their critique of biomass energy companies like Enviva. They point out that the claim of biomass being a carbon-neutral energy source is misleading. When whole trees are used, the carbon sequestration capacity of forests is reduced, and the carbon neutrality of biomass comes into question. This critique challenges the narrative that biomass is an inherently green and sustainable energy source.
The Advocacy for Sustainable Practices
These advocacy groups aren’t just opposing biomass energy; they’re also championing more sustainable practices within the industry. They urge for stricter regulations on the sources of biomass and a more transparent accounting of its environmental impact. Their goal is to ensure that renewable energy sources like biomass contribute positively to environmental conservation and don’t perpetuate ecological damage.
The Role of Policy and Regulation
The debate over biomass energy has significant policy implications. Environmental groups are pushing for stricter regulations on biomass production, including clearer sustainability criteria and more rigorous monitoring of its impact. They argue that such regulations are essential to ensure that renewable energy sources like biomass genuinely contribute to environmental protection and climate change mitigation.
Future Prospects for Biomass Energy and Enviva
The Biomass Energy Industry at a Crossroads
The biomass energy industry, once seen as a key player in the renewable energy sector, is at a crossroads. The challenges faced by Enviva symbolize a broader reevaluation of biomass as a sustainable energy source. The industry must navigate the complex balance between meeting energy needs and ensuring environmental sustainability.
Enviva’s Potential Paths Forward
For Enviva, the path ahead is uncertain, but not without possibilities. The company could pivot towards more sustainable practices, such as ensuring the use of waste wood or exploring new technologies to minimize environmental impact. Alternatively, Enviva might diversify its energy portfolio to include other renewable sources, thereby reducing its reliance on biomass.
Global Energy Policies and Biomass
The future of biomass energy is also tied to global energy policies. Governments around the world, particularly in the EU and Asia, will play a crucial role in shaping the biomass market. Policies that emphasize strict sustainability criteria and carbon accounting could pressure the industry to adopt more environmentally friendly practices.
Innovation and Sustainable Biomass Solutions
Innovation could be a key factor in the survival and evolution of the biomass industry. Developing new technologies that can efficiently convert waste biomass into energy, or advancing carbon capture and storage techniques, could help mitigate the environmental concerns associated with biomass.
The Broader Renewable Energy Landscape
The challenges facing Enviva and the biomass industry also highlight the importance of a diversified approach to renewable energy. Solar, wind, and hydropower are essential components of a comprehensive strategy to transition away from fossil fuels. As the renewable energy landscape evolves, biomass may find its place as part of a broader, more sustainable energy mix.
More To Discover
Conclusion
The story of Enviva serves as a cautionary tale in the renewable energy sector. It underscores the complexities of balancing economic viability with environmental stewardship. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change and sustainable energy, the lessons from Enviva’s rise and struggles will be crucial in guiding future policies and practices in the renewable energy landscape.